Identifying Phase Unbalance Along Distribution Feeders
When load is balanced across the three phases of a distribution feeder the system is more stable, reliable, and efficient. Unbalance causes voltage fluctuations and potential short and long-term reliability problems. Feeder phase balance is often monitored at the substation, but it’s important to also monitor load at additional points along the feeder to ensure balance throughout all segments of feeder.
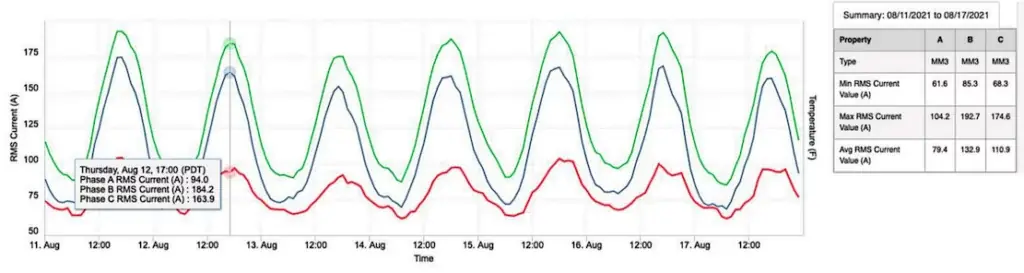
Below is an example of a week of load data for an unbalanced segment of a feeder. These same three phases are balanced at the substation, but at the mid-feeder location below phase A (red line) current is significantly lower than phases B (green) and C (blue).
Sentient Energy’s Grid Analytics SystemTM
The Grid Analytics System solution consists of MM3ai and ZM1 overhead intelligent sensors, UM3+ and UM1 underground intelligent sensors, and the Ample® Analytics Platform. Providing utilities with increased distribution system visibility and actionable insights, the solution improves reliability and allows for data-driven operational decision-making.
How It Works
Sentient Energy’s Grid Analytics System enables utilities to monitor phase balance more thoroughly by capturing load data in more feeder locations using these three steps:
- Deploy sensors – Sensors can be deployed on overhead lines and within underground enclosures to capture load data at programmable intervals. The sensors communicate with Ample software via integrated cellular or mesh wireless communications.
- Identify locations with unbalance – Ample software collects and visualizes sensor data and allows utility operators to identify overloaded segments and phase unbalance.
- Rebalance and continue monitoring – Utilities can make switching changes to improve balance and resume monitoring with Ample to ensure the rebalance is effective.
Results
Sentient Energy’s Grid Analytics System helps facilitate and improve phase balancing at more locations across feeders — improving distribution system efficiency, reliability, and power quality.
